Biological washing powder contains enzymes to help lift stains and get clothes cleaner.
For many, this is enough information. However, it’s also fair to wonder, exactly what enzymes are in biological washing powder. That’s what we discuss below, so read on to find out.
What Enzymes Are in Biological Washing Powder?
Biological washing powder can contain up to five different kinds of enzymes, which are:
- Protease
- Amylase
- Lipase
- Cellulase
- Mannanase
Most household detergents only contain proteases and lipases, as these help break down proteins and fats, respectively.
As you probably know from doing laundry, protein stains (blood, egg, etc.) and fat stains (oils) can be some of the most difficult to remove.
The other enzymes on this list help break down starch, cellulose/plant materials, and mannans, which are found in products such as tree sap.
Generally, these aren’t issues in household laundry but are more common in commercial settings.
How Do Enzymes Work?
The enzymes found in laundry detergent are also found in our bodies, where they do exactly the same thing.
Put simply, enzymes work like tiny scissors – they cut apart bonds between molecules to break them down into simpler components.
This is how they help with stain removal. They break down the protein or fat molecules that are dried into our clothes to help remove the stains, and the remaining components are then all washed away during the rinse cycle.
Where Do Enzymes in Biological Washing Powder Come From?
The enzymes used in biological washing powder come from microorganisms and are produced through fermentation.
Bacteria are fed sugar to ferment before the enzymes are extracted.
What Are the Benefits of Biological Washing Powder?
Biological washing powder can be pretty useful for doing laundry. The benefits of using it over non-bio washing powder include the following.
Washing at lower temperatures
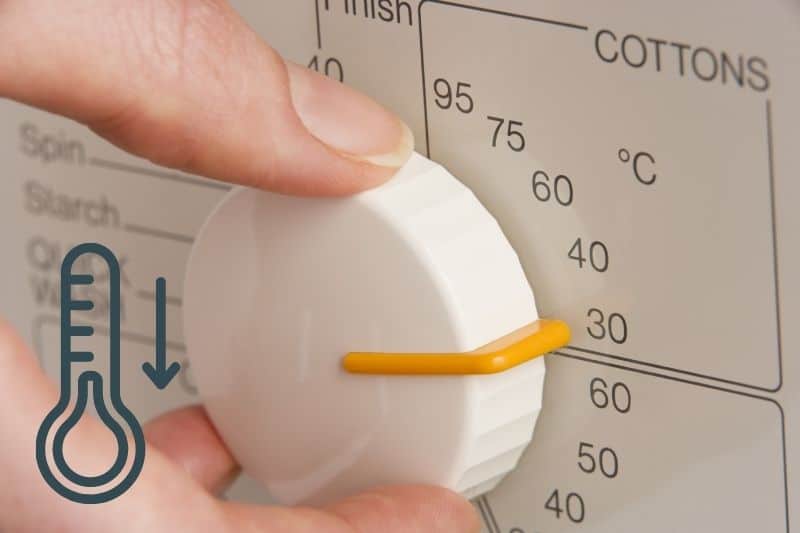

Most enzymatic stains (fats, proteins, etc.) need to be washed at high temperatures to help break down the molecular bonds.
Using biological washing powder means you can wash at lower temperatures simply because they provide superior cleaning performance.
While non-bio detergents still do a good job, biological detergents perform better at lower temperatures.
Considering 60% of CO2 emissions from detergents come from the use phase, reducing the temperature is a good way to save on energy.
Protect delicate fabrics

Generally speaking, biological washing detergents are safe to use on delicate fabrics, such as wool.
It’s worth checking the item’s specific washing instructions, though, especially if the fabric is made from protein, such as silk.
Provided it’s safe to use biological washing powder, it can help you extend the life of delicate fabrics.
It’s also helpful for things like denim, which can lose its colour if washed at too high a temperature. Again, this comes down to you being able to wash the items at low temperatures.
Final Thoughts

You should now have a good idea of what enzymes are in biological washing powder.
As mentioned earlier, household products will often only contain proteases and lipases, although you might find some contain cellulases to help remove grass stains.
Whatever biological washing powder you choose, their superior stain removal at lower temperatures is a major advantage, especially if you have kids who love making a mess!

Jacob is a writer based in Wales, where he lives with his partner and two dogs. All his work is fuelled by extensive research and buckets of coffee.






