Clothes are made from various materials, each chosen to give clothing certain desirable qualities. These fabrics can broadly be split into two categories: natural and synthetic.
This sounds simple enough, but what are synthetics? How do you wash synthetic garments? And are synthetics or natural fibres a better option for your wardrobe?
This article answers all your questions, helping you choose the best fabrics for your clothing and look after them correctly.
What Are Synthetic Fibres?

When humans first started creating fabric, we used natural resources to make the fibres which make up materials.
Examples of natural fibres include cotton from the cotton plant, wool from sheep, and silk from silkworms and other insects. We used the resources of the natural world to make our clothes.
Many of these natural materials are used today. However, we have also seen the rise of synthetic fibres.
Unlike natural fibres, synthetics are artificially made using chemical processes. By artificially creating materials, we can precisely control the characteristics to make them optimal for certain clothing types. For example, super stretchy elastane is perfect for use in swimwear!
10 Examples of Synthetic Fibres in Clothing
Over the years, we have developed many different types of synthetics to fulfil different needs.
These fibres can then be blended with other synthetics or natural fibres to give rise to new materials with unique properties.
In fact, synthetics have become so common in clothing you probably have many items of clothing made from synthetics in your wardrobe.
Take a look at the labels of your clothes and see if you spot any of the below synthetic fibres, the most common synthetics in the UK:
1. Polyester

Polyester is the most popular man-made material in the world!
Short for polyethylene terephthalate, the synthetic was first made in 1941 in the UK. However, it rose to frame in the US in the disco decade of the 1970s.
Its low price, versatility, and wrinkle resistance make it suitable for many clothes. It is often blended with cotton and other synthetic materials.
2. Elastane

Elastane (also known as spandex or lycra) is an elastic material that is added to clothing to give it additional stretch.
These synthetic fibres are so elastic that they can stretch up to seven times their original size! It is typically weaved with other fibres, such as cotton, giving the garment desirable qualities of both fibres. It has the durability and softness of cotton yet the stretch of elastane.
3. Acrylic

Acrylic was first produced from a synthetic polymer called acrylonitrile in the 1940s. It became a popular machine-washable alternative to wool in the 1950 and is still used in sweaters and knitwear today.
The fabric is lightweight and comfortable yet strong enough to withstand daily wear. It is also soft with a wool-like feel but is less breathable than its natural counterpart.
4. Nylon

Another material made from polyamide is nylon. The synthetic material is most famous for its use in women’s stockings but is today used to make shirts, lingerie, swimwear, activewear, and cycling wear.
The synthetic fibres are strong, elastic, and resistant to abrasion, making them the perfect material choice for these garments.
5. Rayon

Rayon is made from cellulose taken from plants. However, just because cellulose is a natural protein, it doesn’t make rayon a natural material.
Extracting cellulose from plants requires chemical processing, making it a semi-synthetic material. Rayon is a more eco-friendly synthetic alternative to silk, with a luxurious appearance and a fluid drape.
6. Acetate

Like rayon, acetate is made from plant-derived cellulose fibres and so is considered a semi-synthetic fibre.
It too has a silk-like appearance and drape, but it is more sensitive to higher temperatures and reacts worse in water.
It is used in a variety of different clothing types, including dresses, blouses, and lingerie, as an affordable silk alternative.
7. Synthetic fur
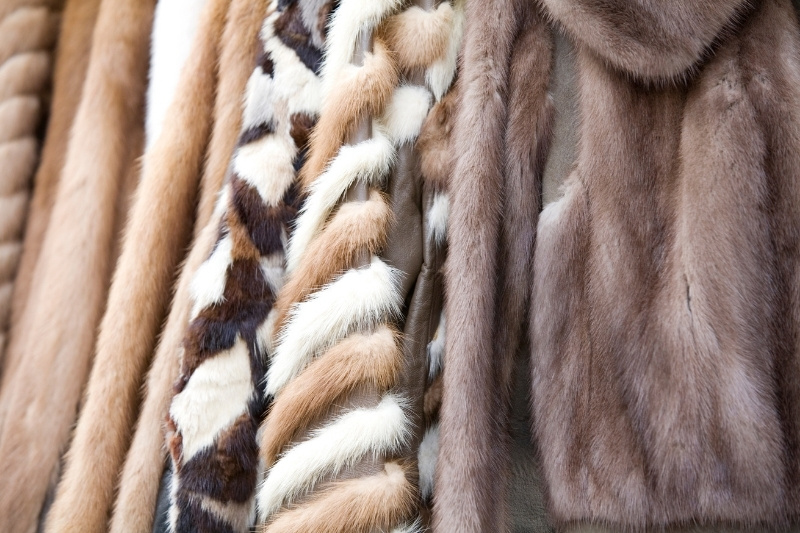

Synthetic fur is precisely as it sounds: material used to replicate the look and feel of animal fur. Also known as faux fur, the material was initially produced as much more affordable than real fur.
In the 1900s, a 10% tax on real fur in Russia meant only the wealthiest could afford a luxurious fur coat! The material is today used as an ethical alternative made without animal products.
8. Neoprene
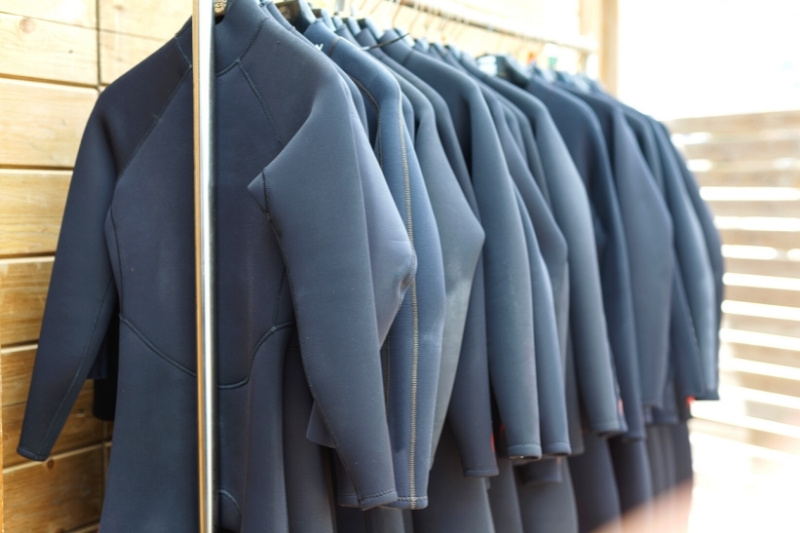

Neoprene is a type of synthetic rubber made from polymerising chloroprene.
You may assume that rubber synthetics have no place in clothing, but you’d be wrong! The material is 100% waterproof and is the perfect material for wetsuits.
It is also a suitable fabric for swimming costumes, water shoes, fishing clothing, and even some jackets.
9. Polyvinyl chloride

Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is another rubbery, waterproof material. It is also resistant to flames, oil, and chemicals!
In clothing, it is better known as “vinyl” and is mainly used to make protective suits for astronauts and firefighters.
However, it is also made to make some high-shine fashion items, such as the iconic 1960s vinyl skirt.
10. Microfibre

Microfibre is a tightly woven yarn made from blending polyester and nylon. The fibres are extremely thin, measuring less than 10 micrometres in diameter!
This small diameter means the fibres can be woven extremely tightly together, making the final material waterproof. This quality makes it a good choice of fabric for sportswear and jackets.
Which Synthetic Fabric Is Best for Clothes?

It is hard to name the single best synthetic fabric for clothes. All synthetics have unique qualities and serve different purposes better.
The fluid silk-like qualities of rayon make it perfect for floaty blouses but a terrible choice for swimwear.
Nylon is a much better option for swimsuits, but it isn’t going to make a good fur jacket. Faux fur made from polyester and acrylic blend is much more suitable.
As you can see, the best synthetic fabric for clothes depends on the type of clothes in question.
What qualities does this garment need? Does it need to be tight or floaty? Does it need to be durable or not? Does it need to be breathable? Waterproof? Stretchy? The best synthetic fabric ticks as many boxes as possible.
More often than not, blended materials are used in clothing to obtain the desired characteristics. These fabrics are made from two or more different fibre types.
For example, polycotton t-shirts are made by blending synthetic polyester with natural cotton. We’ve also already discussed microfibre, a waterproof blend of polyester and nylon.
How Do You Wash Synthetic Clothes?
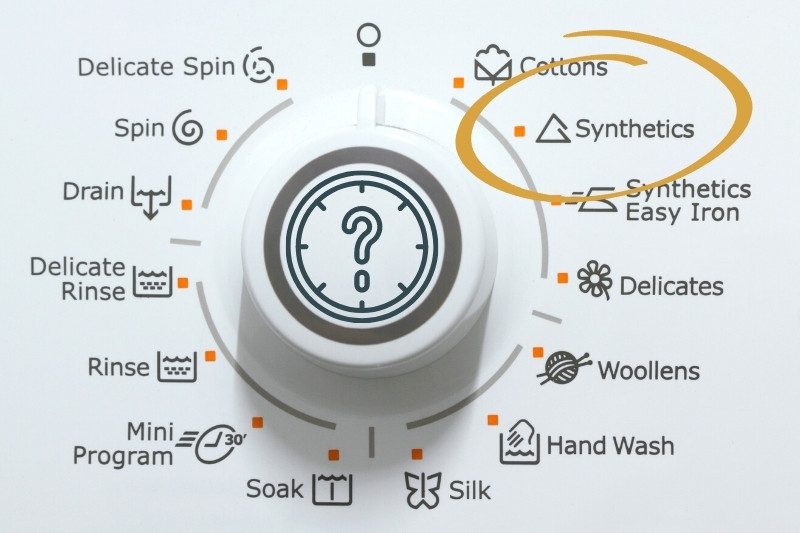
How you wash synthetic clothes depends on the materials in question. For example, the delicate nature of rayon makes it unsuitable for machine washing, and it should only be dry-cleaned or washed by hand. But you’ll be pleased to hear that most synthetics can be washed in the machine.
Nevertheless, there are some things to be aware of before putting your synthetics in the wash. Follow these tips to ensure you look after your clothes, extend their lifespan, and avoid damaging your favourite wardrobe staples:
Beware of high temperatures
As most synthetics are made from plastic polymers, washing at high temperatures can damage or melt the fibres. Therefore, it is always advisable to wash at around 30°C.
You typically cannot tumble-dry synthetics either due to the high heat. The exceptions are polyester, nylon, and acrylic. These are generally safe to put in the tumble dryer but always use low heat.
If in doubt, check the label of your clothing for a recommended temperature. And if your clothes aren’t stained or dirty, you can use a colder temperate than recommended – the number on the label is the maximum the material can withstand. Using a lower temperature is also a great way to save money doing laundry as you’re using less energy.
Use a slower spin speed
You also want to wash synthetics on a slower spin cycle of around 800 to 1,000 RPM. This speed ensures that less durable synthetic materials are not damaged, which could happen if you use a standard cotton programme.
Some washing machines have a special synthetics cycle; if this is available, use it! It adjusts the temperature and spin cycle accordingly.

Reduce microplastic release
As most synthetics are made from plastics, washing releases tiny microplastic pieces that enter our oceans and pollute our environment.
Washing at a lower temperature and slower spin can reduce the number of microplastics released.
Other ways you can try and make your washing more eco-friendly include:
- Only washing your synthetic clothes when they are truly dirty and need a wash. You can remove odours by letting your clothes air and remove stains by hand.
- Washing full loads to reduce how much your clothes bang around in the machine. The more they bang, the more friction there is and the greater the microplastic release.
- Putting your washing machine on a shorter cycle. The less time your synthetics have in the machine, the less time there is for fibres to break and microplastics to be released.

Hannah has a passion for cleaning. She worked her way around Australia by cleaning hostels in exchange for free accommodation and used her cleaning skills to bag a job as a chalet host for a luxury ski company in France.






